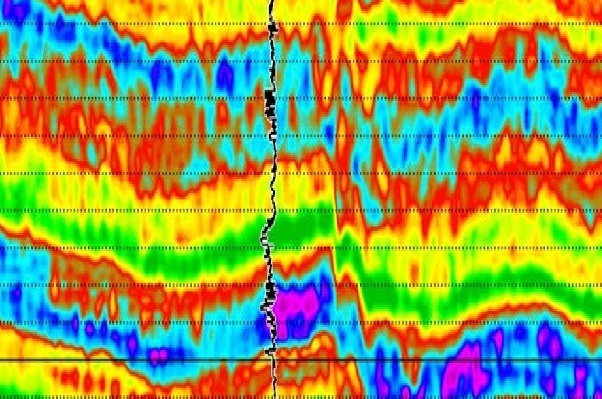
Beneath the Earth’s surface lies a vast and intricate landscape of rock formations, each with its unique properties and characteristics. Exploring and understanding these geological structures is crucial for various industries, from oil and gas exploration to environmental studies. One powerful tool that aids in unravelling the secrets hidden beneath the Earth’s crust is seismic inversion. In this article, we will delve into the world of seismic inversion and its role in revealing the rock properties that shape our planet.
Table of Contents
The Basics of Seismic Inversion
1. Seismic Imaging:
Seismic inversion workflow is a technique used in geophysics to transform seismic data into a more detailed and accurate representation of subsurface rock properties. Seismic surveys involve sending waves of energy into the Earth and recording the reflections that bounce back. These reflections are then analysed to create an image of the subsurface.
2. The Need for Inversion
While seismic imaging provides a broad view of the subsurface, inversion is necessary to extract quantitative information about the properties of the rocks. Seismic inversion helps researchers and geoscientists create high-resolution models of the subsurface, allowing for a more precise understanding of the geological formations.
Rock Properties Revealed
1. P-Wave and S-Wave Velocity
Seismic waves come in two main types: compressional (P-waves) and shear (S-waves). These waves travel through the subsurface at different velocities depending on the rock properties. Seismic inversion allows scientists to discern the P-wave and S-wave velocities, providing insights into the elastic properties of rocks.
2. Porosity and Permeability
Porosity, the measure of void spaces in a rock, and permeability, the ability of fluids to flow through a rock, are critical parameters in hydrocarbon exploration. Seismic inversion helps estimate these properties by analysing how seismic waves propagate through different rock types. This information is invaluable for assessing the potential of underground reservoirs.
3. Lithology and Stratigraphy
Seismic inversion aids in identifying different rock types (lithology) and their layering (stratigraphy). By analysing the amplitude and frequency of seismic reflections, geoscientists can distinguish between sandstones, shales, and other geological formations, providing a detailed picture of the subsurface structure.
4. Fluid Content and Saturation
The presence of fluids, such as oil, gas, or water, significantly affects seismic wave behaviour. Seismic inversion helps determine the fluid content and saturation within rocks. This information is crucial for predicting the productivity of reservoirs and optimizing resource extraction processes.
Applications and Industry Impact
1. Oil and Gas Exploration
In the oil and gas industry, seismic inversion plays a pivotal role in identifying potential hydrocarbon reservoirs. Accurate knowledge of rock properties helps companies make informed decisions about drilling locations, reservoir size, and production strategies.
2. Geothermal and Environmental Studies
Seismic inversion is not limited to fossil fuel exploration. It is increasingly used in geothermal energy exploration and environmental studies. Understanding subsurface rock properties aids in sustainable resource development and environmental impact assessments.
3. Engineering and Infrastructure Planning
In civil engineering, seismic inversion assists in assessing the stability of the Earth’s crust for infrastructure projects. By understanding the geological properties of the subsurface, engineers can design structures that withstand seismic events more effectively.
Seismic inversion serves as a powerful tool in unravelling the mysteries of the Earth’s subsurface. By revealing intricate details about rock properties, this technique has far-reaching applications in diverse industries. As technology advances, seismic inversion continues to evolve, offering unprecedented insights that contribute to the sustainable development of our planet’s resources and the betterment of society.